Modified True/False
Indicate
whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make
the statement true.
|
|
|
1.
|
A property that can only be observed when one substance changes into a different
substance is called a chemical property. _________________________
|
|
|
2.
|
On the periodic table, metals are found, in general, on the left side of
the table. _________________________
|
|
|
3.
|
Solid elements described as dull, brittle, and poor electrical and thermal
conductors are most likely metals. _________________________
|
|
|
4.
|
The group of elements that tend to be found as toxic gases or liquids in their
pure form, including chlorine, bromine and iodine, are called the alkali metals.
_________________________
|
Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
5.
|
A period’s number on the periodic table corresponds to the number
of:
a. | electrons an atom in the period can accept when reacting to form
compounds. | b. | energy levels of the atoms in the period. | c. | compounds that may
be formed by an element in the period. | d. | neutrons in the nuclei of atoms in the
period. |
|
|
|
6.
|
An example of a chemical property of a substance is its:
a. | melting point. | b. | specific heat. | c. | reaction
rate. | d. | density. |
|
|
|
7.
|
Horizontal rows on the periodic table are called:
a. | periods. | b. | groups. | c. | columns. | d. | boxes. |
|
|
|
8.
|
All of the following are characteristics of metals EXCEPT:
a. | shiny. | b. | good conductors. | c. | ductile. | d. | brittle. |
|
|
|
9.
|
Characteristics of non-metals include all of the following EXCEPT:
a. | ductile. | b. | brittle. | c. | poor
conductors. | d. | dull. |
|
|
|
10.
|
The location of metals on the periodic table is on the:
a. | left. | b. | top. | c. | right. | d. | bottom. |
|
|
|
11.
|
Most non-metals on the periodic table are located on the:
a. | left. | b. | bottom. | c. | right. | d. | top. |
|
|
|
12.
|
An atomic mass unit is the approximate mass of a single:
a. | electron. | b. | proton. | c. | carbon
atom. | d. | carbon molecule. |
|
|
|
13.
|
An example of a metalloid, elements with properties between metals and
non-metals, is
a. | iron. | b. | silicon. | c. | oxygen. | d. | copper. |
|
|
|
14.
|
Atomic weight is approximately the same as:
a. | the atomic number. | b. | an atomic mass unit. | c. | the mass
number. | d. | the element symbol. |
|
|
|
15.
|
The diagram below represents information that can be found on the periodic table
for the element helium. 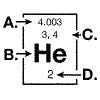 The atomic weight of a helium atom is
indicated by the arrow at:
|
|
|
16.
|
The diagram below represents information that can be found on the periodic table
for the element argon. 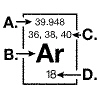 The mass number for an argon isotope is
represented at:
|
|
|
17.
|
The diagram below represents an atom containing 4 electrons in the third energy
level. The small, dark circles represent electrons distributed around the nucleus of the atom. The
element represented by the diagram below is: 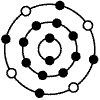 a. | silicon. | b. | carbon. | c. | beryllium. | d. | chromium. |
|
|
|
18.
|
The second energy level of a single oxygen atom contains six electrons. The
total number of electrons found on an oxygen atom is:
|
|
|
19.
|
The total number of electrons the first three energy levels of an atom can hold
is:
|
|
|
20.
|
Electrons are found in the third energy level for atoms of the element:
a. | sodium. | b. | sulfur. | c. | boron. | d. | lithium. |
|
|
|
21.
|
All of the following statements about electron levels are true EXCEPT:
a. | Electrons in the outermost level have the highest energy. | b. | The most active
elements have outermost electron levels filled. | c. | Outermost electrons are the electrons that
interact with other atoms. | d. | Electrons in completely filled levels do not
participate in forming chemical bonds. |
|
|
|
22.
|
The diagram below represents information that can be found on the periodic table
for the element magnesium. 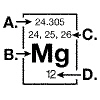 The atomic number for magnesium is
indicated at:
|
|
|
The Periodic Table
of the Elements
| | 1
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 18
| 1
| 1
H
Hydrogen
1.0 | 2
| | | | | | | | | | | 13
| 14
| 15
| 16
| 17
| 2
He
Helium
4.0 | 2
|
3
Li
Lithium
6.9 | 4
Be
Beryllium
9.0 | | | | | | | | | | | 5
B
Boron
10.8 | 6
C
Carbon
12.0 | 7
N
Nitrogen
14.0 | 8
O
Oxygen
16.0 | 9
F
Fluorine
19.0 | 10
Ne
Neon
20.2 | 3
|
11
Na
Sodium
23.0 | 12
Mg
Magnesium
24.3 | 3
| 4
| 5
| 6
| 7
| 8
| 9
| 10
| 11
| 12
| 13
Al
Aluminum
27.0 | 14
Si
Silicon
28.1 | 15
P
Phosphorus
31.0 | 16
S
Sulfur
32.1 | 17
Cl
Chlorine
35.5 | 18
Ar
Argon
39.9 | 4
|
19
K
Potassium
39.1 | 20
Ca
Calcium
40.1 | 21
Sc
Scandium
45.0 | 22
Ti
Titanium
47.9 | 23
V
Vanadium
50.9 | 24
Cr
Chromium
52.0 | 25
Mn
Manganese
54.9 | 26
Fe
Iron
55.8 | 27
Co
Cobalt
58.9 | 28
Ni
Nickel
58.7 | 29
Cu
Copper
63.5 | 30
Zn
Zinc
65.4 | 31
Ga
Gallium
69.7 | 32
Ge
Germanium
72.6 | 33
As
Arsenic
74.9 | 34
Se
Selenium
79.0 | 35
Br
Bromine
79.9 | 36
Kr
Krypton
83.8 | 5
|
37
Rb
Rubidium
85.5 | 38
Sr
Strontium
87.6 | 39
Y
Yttrium
88.9 | 40
Zr
Zirconium
91.2 | 41
Nb
Niobium
92.9 | 42
Mo
Molybdenum
95.9 | 43
Tc
Technetium
(97.9) | 44
Ru
Ruthenium
101.1 | 45
Rh
Rhodium
102.9 | 46
Pd
Palladium
106.4 | 47
Ag
Silver
107.9 | 48
Cd
Cadmium
112.4 | 49
In
Indium
114.8 | 50
Sn
Tin
118.7 | 51
Sb
Antimony
121.8 | 52
Te
Tellurium
127.6 | 53
I
Iodine
126.9 | 54
Xe
Xenon
131.3 | 6
|
55
Cs
Cesium
132.9 | 56
Ba
Barium
137.3 | 57
La
Lanthanum
138.9 | 72
Hf
Hafnium
178.5 | 73
Ta
Tantalum
180.9 | 74
W
Tungsten
183.8 | 75
Re
Rhenium
186.2 | 76
Os
Osmium
190.2 | 77
Ir
Iridium
192.2 | 78
Pt
Platinum
195.1 | 79
Au
Gold
197.0 | 80
Hg
Mercury
200.6 | 81
Tl
Thallium
204.4 | 82
Pb
Lead
207.2 | 83
Bi
Bismuth
209.0 | 84
Po
Polonium
(209.0) | 85
At
Astatine
(210.0) | 86
Rn
Radon
(222.0) | 7
|
87
Fr
Francium
(223.0) | 88
Ra
Radium
(226.0) | 89
Ac
Actinium
(227.0) | 104
Rf
Rutherfordium
(261.1) | 105
Db
Dubnium
(262.1) | 106
Sg
Seaborgium
(263.1) | 107
Bh
Bohrium
(262.1) | 108
Hs
Hassium
(265) | 109
Mt
Meitnerium
(266) | 110
Uun
Ununnilium
(271) | 111
Uuu
Unununium
(272) | 112
Uub
Ununbium
(277) | | 114
Uuq
Ununquadium
(285) | | 116
Uuh
Ununhexium
(289) | | 118
Uuo
Ununoctium
(293) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 58
Ce
Cerium
140.1 | 59
Pr
Praseodymium
140.9 | 60
Nd
Neodymium
144.2 | 61
Pm
Promethium
(144.9) | 62
Sm
Samarium
150.4 | 63
Eu
Europium
152.0 | 64
Gd
Gadolinium
157.3 | 65
Tb
Terbium
158.9 | 66
Dy
Dysprosium
162.5 | 67
Ho
Holmium
164.9 | 68
Er
Erbium
167.3 | 69
Tm
Thulium
168.9 | 70
Yb
Ytterbium
173.0 | 71
Lu
Lutetium
175.0 | | | | |
90
Th
Thorium
232.0 | 91
Pa
Protactinium
231.0 | 92
U
Uranium
238.0 | 93
Np
Neptunium
(237.0) | 94
Pu
Plutonium
244.1 | 95
Am
Americium
(243.1) | 96
Cm
Curium
(247.1) | 97
Bk
Berkelium
(247.1) | 98
Cf
Californium
(251.1) | 99
Es
Einsteinium
(252.1) | 100
Fm
Fermium
(257.1) | 101
Md
Mendelevium
(258.1) | 102
No
Nobelium
(259.1) | 103
Lr
Lawrencium
(262.1) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Figure 7-1
|
|
|
23.
|
According to the periodic table in Figure 7-1, which group are the chemical
elements that belong to the noble gases?
|
|
|
24.
|
According to the periodic table in Figure 7-1, the group known as the halogens
include the element:
a. | sodium. | b. | calcium. | c. | chlorine. | d. | phosphorus. |
|
|
|
25.
|
Using the periodic table in Figure 7-1, transition elements belong to
groups:
a. | 1-8 | b. | 3-12 | c. | 10-15 | d. | 13-18 |
|
|
|
26.
|
Using the periodic table in Figure 7-1, all of the following elements belong to
the main group elements EXCEPT:
a. | hydrogen. | b. | radium. | c. | aluminum. | d. | iron. |
|
|
|
27.
|
According to the periodic table in Figure 7-1, transition metals include all of
the following elements EXCEPT:
a. | potassium. | b. | iron. | c. | copper. | d. | gold. |
|
|
|
28.
|
Alkali metals, highly reactive with oxygen, are found on the periodic table in
Figure 7-1 in group:
|
|
|
29.
|
The atomic weight of boron is 10.811. What is the mass number of the most
abundant isotope of boron?
|
Completion
Complete each
statement.
|
|
|
Select the correct term to complete each sentence. There are extra terms in
the list.| groups | rows | periods | | noble | halogens | metalloids | | alkali | nonmetals | periodicity | | | |
|
|
|
30.
|
The group identified as inert gases because their atoms do not form chemical
bonds with other atoms is also known as the ____________________ gases.
|
|
|
31.
|
Horizontal rows on the periodic table are called ____________________.
|
|
|
32.
|
On the periodic table, elements with similar properties are placed in vertical
columns called ____________________.
|
|
|
33.
|
Elements on the periodic table that have properties between metals and
non-metals are called ____________________
|
|
|
34.
|
Helium belongs to the vertical group on the periodic table known as the
____________________.
|
|
|
35.
|
The most active metal is found in the group known as the ____________________
metals.
|
Short Answer
|
|
|
36.
|
Two particles found in the nucleus of most atoms have masses equivalent to one
atomic mass unit, or 1 amu. Name the particles.
|
|
|
37.
|
Chemical and physical changes represent two ways in which a substance may be
altered. Which change is more difficult to reverse?
|
|
|
38.
|
Some elements occur naturally while others are made by scientists in the
laboratory. Of which is there a greater number: man-made or naturally-occurring elements?
|
|
|
39.
|
The periodic table was developed by scientists over a number of years after much
investigation.What properties were used to organize the periodic table?
|
Problem
|
|
|
40.
|
Use the periodic table below to answer the following questions: The Periodic Table of the
Elements
| | 1
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 18
| 1
| 1
H
Hydrogen
1.0 | 2
| | | | | | | | | | | 13
| 14
| 15
| 16
| 17
| 2
He
Helium
4.0 | 2
|
3
Li
Lithium
6.9 | 4
Be
Beryllium
9.0 | | | | | | | | | | | 5
B
Boron
10.8 | 6
C
Carbon
12.0 | 7
N
Nitrogen
14.0 | 8
O
Oxygen
16.0 | 9
F
Fluorine
19.0 | 10
Ne
Neon
20.2 | 3
|
11
Na
Sodium
23.0 | 12
Mg
Magnesium
24.3 | 3
| 4
| 5
| 6
| 7
| 8
| 9
| 10
| 11
| 12
| 13
Al
Aluminum
27.0 | 14
Si
Silicon
28.1 | 15
P
Phosphorus
31.0 | 16
S
Sulfur
32.1 | 17
Cl
Chlorine
35.5 | 18
Ar
Argon
39.9 | 4
|
19
K
Potassium
39.1 | 20
Ca
Calcium
40.1 | 21
Sc
Scandium
45.0 | 22
Ti
Titanium
47.9 | 23
V
Vanadium
50.9 | 24
Cr
Chromium
52.0 | 25
Mn
Manganese
54.9 | 26
Fe
Iron
55.8 | 27
Co
Cobalt
58.9 | 28
Ni
Nickel
58.7 | 29
Cu
Copper
63.5 | 30
Zn
Zinc
65.4 | 31
Ga
Gallium
69.7 | 32
Ge
Germanium
72.6 | 33
As
Arsenic
74.9 | 34
Se
Selenium
79.0 | 35
Br
Bromine
79.9 | 36
Kr
Krypton
83.8 | 5
|
37
Rb
Rubidium
85.5 | 38
Sr
Strontium
87.6 | 39
Y
Yttrium
88.9 | 40
Zr
Zirconium
91.2 | 41
Nb
Niobium
92.9 | 42
Mo
Molybdenum
95.9 | 43
Tc
Technetium
(97.9) | 44
Ru
Ruthenium
101.1 | 45
Rh
Rhodium
102.9 | 46
Pd
Palladium
106.4 | 47
Ag
Silver
107.9 | 48
Cd
Cadmium
112.4 | 49
In
Indium
114.8 | 50
Sn
Tin
118.7 | 51
Sb
Antimony
121.8 | 52
Te
Tellurium
127.6 | 53
I
Iodine
126.9 | 54
Xe
Xenon
131.3 | 6
|
55
Cs
Cesium
132.9 | 56
Ba
Barium
137.3 | 57
La
Lanthanum
138.9 | 72
Hf
Hafnium
178.5 | 73
Ta
Tantalum
180.9 | 74
W
Tungsten
183.8 | 75
Re
Rhenium
186.2 | 76
Os
Osmium
190.2 | 77
Ir
Iridium
192.2 | 78
Pt
Platinum
195.1 | 79
Au
Gold
197.0 | 80
Hg
Mercury
200.6 | 81
Tl
Thallium
204.4 | 82
Pb
Lead
207.2 | 83
Bi
Bismuth
209.0 | 84
Po
Polonium
(209.0) | 85
At
Astatine
(210.0) | 86
Rn
Radon
(222.0) | 7
|
87
Fr
Francium
(223.0) | 88
Ra
Radium
(226.0) | 89
Ac
Actinium
(227.0) | 104
Rf
Rutherfordium
(261.1) | 105
Db
Dubnium
(262.1) | 106
Sg
Seaborgium
(263.1) | 107
Bh
Bohrium
(262.1) | 108
Hs
Hassium
(265) | 109
Mt
Meitnerium
(266) | 110
Uun
Ununnilium
(271) | 111
Uuu
Unununium
(272) | 112
Uub
Ununbium
(277) | | 114
Uuq
Ununquadium
(285) | | 116
Uuh
Ununhexium
(289) | | 118
Uuo
Ununoctium
(293) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 58
Ce
Cerium
140.1 | 59
Pr
Praseodymium
140.9 | 60
Nd
Neodymium
144.2 | 61
Pm
Promethium
(144.9) | 62
Sm
Samarium
150.4 | 63
Eu
Europium
152.0 | 64
Gd
Gadolinium
157.3 | 65
Tb
Terbium
158.9 | 66
Dy
Dysprosium
162.5 | 67
Ho
Holmium
164.9 | 68
Er
Erbium
167.3 | 69
Tm
Thulium
168.9 | 70
Yb
Ytterbium
173.0 | 71
Lu
Lutetium
175.0 | | | | |
90
Th
Thorium
232.0 | 91
Pa
Protactinium
231.0 | 92
U
Uranium
238.0 | 93
Np
Neptunium
(237.0) | 94
Pu
Plutonium
244.1 | 95
Am
Americium
(243.1) | 96
Cm
Curium
(247.1) | 97
Bk
Berkelium
(247.1) | 98
Cf
Californium
(251.1) | 99
Es
Einsteinium
(252.1) | 100
Fm
Fermium
(257.1) | 101
Md
Mendelevium
(258.1) | 102
No
Nobelium
(259.1) | 103
Lr
Lawrencium
(262.1) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| a. In which group are the alkali metals located? | _____ | | b. In which group are
the noble gases located? | _____ | | c. In which group are the halogens located? | _____ | | d. In which groups are the transition metals located? | _____ | | e. How many energy
levels are in a calcium atom? | _____ | | |
|
|
|
41.
|
An atomic mass unit is equal to 1.66 ´
10-24 grams. What is the mass, in grams, of an average fluorine atom?
|
Essay
|
|
|
42.
|
Each element is represented on the periodic table by a box containing numbers
and a letter or letters. Explain what is meant by each number and the letters for the element sodium,
which is represented in the following diagram. 
|
|
|
43.
|
The atomic weight of carbon is 12.011. Explain how this number is
established.
|