Modified True/False
Indicate
whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make
the statement true.
|
|
|
1.
|
Two negative charges will attract one another.
_________________________
|
|
|
2.
|
The smallest quantity of electric charge that can be found in ordinary matter is
represented by the letter c. _________________________
|
|
|
3.
|
The majority of ordinary matter has a net charge of zero.
_________________________
|
|
|
4.
|
The number of protons plus the number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom is
known as the mass number. _________________________
|
|
|
5.
|
The tiny core of an atom containing most of the mass of the atom is the
neutron. _________________________
|
|
|
6.
|
The nucleus of an atom that spontaneously breaks up to emits particles or pure
energy may be called radioactive. _________________________
|
Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
7.
|
The fundamental property of matter that may be identified as positive or
negative is:
a. | magnetism. | b. | mass. | c. | electric
charge. | d. | gravitational force. |
|
|
|
8.
|
The scientist who suggested that atoms contain a hard core containing most of
the mass of an atom was:
a. | J.J. Thompson. | b. | Ernest Rutherford. | c. | Hans
Geiger. | d. | Ernest Marsdan. |
|
|
|
9.
|
A particle with zero charge found in the nucleus of an atom is called
a(n):
a. | electron. | b. | proton. | c. | neutron. | d. | positron |
|
|
|
10.
|
The charge on a proton is:
|
|
|
11.
|
The mass of an electron is about:
a. | 1800 times heavier than a proton. | b. | 1800 times lighter than a
proton. | c. | 10,000 times heavier than a proton. | d. | 10,000 times lighter than a
proton. |
|
|
|
12.
|
Protons in the nucleus of an atom are held together by:
a. | electromagnetic force. | b. | gravitational force. | c. | strong nuclear
force. | d. | weak force. |
|
|
|
13.
|
Electrons are held in place outside the nucleus by:
a. | electromagnetic force. | b. | gravitational force. | c. | strong nuclear
force. | d. | weak force. |
|
|
|
14.
|
A force which may cause a neutron to break apart forming an electron and
proton is the:
a. | electromagnetic force. | b. | gravitational force. | c. | strong nuclear
force. | d. | weak force |
|
|
|
15.
|
The number of protons in an atom is the:
a. | atomic weight. | b. | mass number. | c. | atomic
number. | d. | atomic mass |
|
|
|
16.
|
The particle with about the same mass as the proton found in the nucleus is
the:
a. | electron. | b. | proton. | c. | neutron. | d. | positron. |
|
|
|
17.
|
An atom with the proper combination of protons and neutrons in its nucleus will
not break apart spontaneously. Such an atom may be described as:
a. | radioactive. | b. | unstable. | c. | decaying. | d. | stable. |
|
|
|
18.
|
Atoms of the same element whose nucleus contains different numbers of neutrons
are called:
a. | isotopes. | b. | nucleotides. | c. | spectrums. | d. | isobars. |
|
|
|
19.
|
The tiny core of an atom containing most of the mass of the atom and all of its
positive charge is called the:
a. | proton. | b. | neutron. | c. | electron. | d. | nucleus. |
|
|
|
20.
|
The scientist given credit for identifying the neutron is:
a. | J.J. Thomson. | b. | Ernest Rutherford. | c. | James
Chadwick. | d. | Albert Einstein |
|
|
|
21.
|
The mass of an atom is determined mainly by the:
a. | mass of the neutrons. | b. | mass of the neutrons and
protons. | c. | mass of the electrons. | d. | mass of the electrons and
neutrons. |
|
|
|
22.
|
The letter e represents the elementary charge. In normal matter,
the charge that would not be found is:
|
|
|
23.
|
The diagrams below, in which arrows indicate the direction of movement,
represent charged particles placed near one another. The diagram that correctly represents the motion
of the charged particles is: 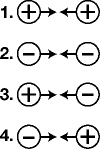
|
|
|
24.
|
A particle containing charges of +8e and -2e will
have a net charge of:
|
|
|
25.
|
Susan walks across a carpet. Her body picks up excess electrons and a
charge that is:
a. | zero. | b. | positive. | c. | neutral. | d. | negative |
|
|
|
26.
|
J.J. Thomson is given credit for the discovery of a particle smaller than an
atom, the:
a. | negatively charged electron. | b. | positively charged proton. | c. | neutral
neutron. | d. | positively charged alpha particle. |
|
|
|
27.
|
A charged particle that accounts for nearly half the mass of an atom is
the:
a. | electron. | b. | neutron. | c. | proton. | d. | positron. |
|
|
|
28.
|
The particle found in the nucleus of all atoms is:
a. | proton. | b. | neutron. | c. | electron. | d. | positron. |
|
|
|
29.
|
Of the particles listed below, the most massive is the:
a. | proton. | b. | neutron. | c. | electron. | d. | positron. |
|
|
|
30.
|
Of the following statements, the one which is ALWAYS TRUE is:
a. | All lithium atoms contain the same number of protons. | b. | All lithium atoms
contain the same number of neutrons. | c. | All lithium atoms have the same
mass. | d. | The sum of protons plus neutrons is the same in all lithium
atoms. |
|
|
|
31.
|
Atoms of the same element may contain:
a. | the same number of neutrons but a different number of protons. | b. | the same number of
protons but a different number of neutrons. | c. | a different number of protons and a different
number of neutrons. | d. | the same number of electrons but a different
number of protons. |
|
|
|
32.
|
In a carbon atom with a mass number of 14 and an atomic number of 6, the number
of protons is:
|
|
|
33.
|
In a carbon atom with a mass number of 14 and an atomic number of 6, the number
of neutrons is:
|
|
|
34.
|
An atom of silicon contains 14 protons and 16 neutrons.The mass number
is:
|
|
|
35.
|
Alpha decay of an atom produces all of the following decreases in the atom
EXCEPT:
a. | decrease of protons by 2. | b. | decrease of neutrons by 2. | c. | decrease of atomic
number by 2. | d. | decrease of mass number by 2. |
|
|
|
36.
|
Beta decay in the nucleus of an atom produces all of the following changes
EXCEPT:
a. | increase of protons by 1. | b. | decrease of neutrons by 1. | c. | increase in atomic
number by 1. | d. | increase in mass number by 1. |
|
|
|
37.
|
As Carmine combs her hair, her comb acquires electrons from her hair. The net
charge on her hair becomes:
a. | positive. | b. | negative. | c. | zero. | d. | neutral. |
|
|
|
38.
|
Radium-226 decays radioactively to become radon-222 by a process known
as:
a. | alpha decay. | b. | beta decay. | c. | gamma
decay. | d. | fission. |
|
|
|
39.
|
The radioactive decay of lead-214 to become bismuth-214 occurs due to:
a. | alpha decay. | b. | beta decay. | c. | gamma
decay. | d. | fission. |
|
Completion
Complete each
statement.
|
|
|
Select the correct term to complete each sentence. There are extra terms in
the list.| alpha | beta | spectroscope | | neutral | charged | isotopes | | 2 | 6 | 8 | | strong
nuclear | gravitational | weak | | | |
|
|
|
40.
|
When the total charge on an object is zero, the object is electrically
____________________.
|
|
|
41.
|
Atoms having the same atomic number but different mass numbers are described as
____________________.
|
|
|
42.
|
The force which holds the nucleus together is the _________________________
force.
|
|
|
43.
|
The radioactive decay of an atom resulting in the decrease in the atomic number
with no change in the atomic mass is ____________________ decay.
|
Short Answer
|
|
|
44.
|
How do electric and gravitational forces differ?
|
|
|
45.
|
Where would a particle with a charge of +e be found in an
atom?
|
|
|
46.
|
A bismuth atom which contains 83 protons and 127 neutrons decays to produce an
atom of polonium with a mass number of 210 and 84 protons. What type of decay does bismuth
experience?
|
Problem
|
|
|
47.
|
The mass number for an isotope of oxygen is 17 and the atomic number is 8. How
many neutrons are present in this isotope of oxygen?
|
|
|
48.
|
The diagram below represents the charge distribution of positive and negative
charges in a body. 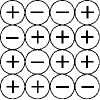 What is the overall (net) charge on the
object as it is pictured?
|
|
|
49.
|
Uranium, with 92 protons and 146 neutrons, undergoes alpha decay and becomes
thorium. How many protons and neutrons are present in the isotope of thorium produced by this
decay?
|
|
|
50.
|
A lead atom, with 82 protons and 128 neutrons, decays to produce an atom of
bismuth with a mass number of 210. How many neutrons are in the nucleus of the isotope of bismuth
produced?
|
Essay
|
|
|
51.
|
Describe the difference between an electron and a proton. In your description
tell (1) where each is found in the nucleus (2) the charge, if any, on each and (3) how their masses
compare.
|
|
|
52.
|
How is the atom of one element different from the atom of another
element?
|
|
|
53.
|
Describe how two neutral objects may become positively and negatively
charged.
|