Modified True/False
Indicate
whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make
the statement true.
|
|
|
1.
|
The transfer of heat through the motion of fluids such as air and water is
conduction. _________________________
|
|
|
2.
|
Ice floats on water because it has a lower freezing point than water.
_________________________
|
|
|
3.
|
Liquid molecules have more energy than solid molecules.
_________________________
|
Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
4.
|
A fluid is a form of matter that includes:
a. | solids only. | b. | liquids only. | c. | both liquids and
solids. | d. | both liquids and gases. |
|
|
|
5.
|
The temperature at which a solid changes to a liquid is called the:
a. | boiling point. | b. | melting point. | c. | condensation
point. | d. | freezing point. |
|
|
|
6.
|
In which phase of matter are molecules or atoms most restricted in their
ability to move?
a. | Plasma | b. | Solid | c. | Liquid | d. | Gas |
|
|
|
7.
|
The name for air that contains water vapor in equilibrium at a certain
temperature is:
a. | evaporated. | b. | condensed. | c. | saturated. | d. | relative
humidity. |
|
|
|
8.
|
The factor most directly responsible for Earth’s atmospheric pressure
is:
a. | gravity. | b. | intermolecular forces. | c. | bonding forces
between molecules. | d. | the presence of argon in the
air. |
|
|
|
9.
|
The most abundant material in Earth’s atmosphere is:
a. | oxygen. | b. | nitrogen. | c. | carbon
dioxide. | d. | hydrogen. |
|
|
|
10.
|
The phase of matter in which atoms are free to move but don’t have enough
energy to completely break bonds is:
a. | solid. | b. | liquid. | c. | gas. | d. | plasma. |
|
|
|
11.
|
An applied force causes pressure that acts in all direction when the force is
applied to:
a. | both liquids and solids. | b. | solids only. | c. | both liquids and
gases. | d. | gases only. |
|
|
|
12.
|
Which statement best describes intermolecular forces?
a. | Intermolecular forces are stronger than bonding forces. | b. | Intermolecular
forces act within molecules. | c. | Intermolecular forces are only
attractive. | d. | Intermolecular forces may be both attractive and
repulsive. |
|
|
|
13.
|
Intermolecular forces are completely overcome:
a. | in solids. | b. | in liquids. | c. | in
gases. | d. | in all phases. |
|
|
|
14.
|
Water has a lower melting point than iron because:
a. | water has more thermal energy. | b. | water has stronger intermolecular
forces. | c. | water has weaker intermolecular forces. | d. | water has lower
density than iron. |
|
|
|
15.
|
When athletes exercise hard, their bodies sweat. On a breezy day, a sweating
athlete will:
a. | feel cooler as the sweat evaporates. | b. | feel warmer as the sweat
evaporates. | c. | feel cooler as the sweat condenses. | d. | be unaffected by the
sweat. |
|
|
|
16.
|
Heat is added slowly to a block of ice at 0ºC. While the ice is melting,
the temperature of the block:
a. | remains the same. | b. | slowly increases. | c. | rapidly
increases. | d. | slowly decreases. |
|
|
|
17.
|
Ice floats in water because:
a. | its molecules are tightly packed. | b. | the density of liquid water is lower than solid
ice. | c. | water below it remains at a temperature above 0ºC. | d. | liquid water expands
as it freezes. |
|
|
|
18.
|
When molecules change from liquid to gas at temperatures below the boiling
point, the change is called:
a. | melting. | b. | freezing. | c. | evaporation. | d. | condensation. |
|
|
|
19.
|
The diagram shows the transfer of heat due to the movement of air near a
lake. 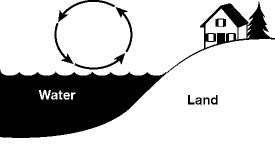 The name given to the type of heat
transfer in the diagram is: a. | natural conduction. | b. | natural convection. | c. | natural
condensation. | d. | forced conduction. |
|
|
|
A material cools from being a gas at a temperature at 160ºC to being a
solid at a temperature of 20ºC. The diagram below represents a graph of the data for these
changes. 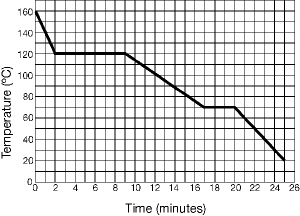 Figure 5-1A Figure 5-1A
|
|
|
20.
|
In Figure 5-1A, the temperature at which the material is ALL solid is:
a. | 40ºC | b. | 70ºC | c. | 100ºC | d. | 120ºC |
|
|
|
21.
|
Referring to Figure 5-1A, what is the physical state of the material at
70ºC?
a. | Solid | b. | Solid and liquid | c. | Liquid | d. | Liquid and gas |
|
|
|
22.
|
As some gas molecules of a material condense to become a liquid, the
average molecules of gas remaining are:
a. | closer together. | b. | faster moving. | c. | slower
moving. | d. | unchanged. |
|
|
|
23.
|
Which graph best represents the relationship between temperature of the air and
the rate of evaporation of water? 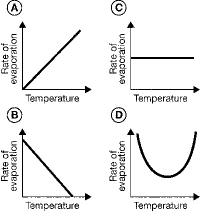
|
Completion
Complete each
statement.
|
|
|
Select the correct term to complete each sentence. There are extra terms in
the list.| gravitational | intermolecular | oxygen | | nitrogen | conduction | convection | | liquid | solid | brittle | | elastic | crystalline | amorphous | | equilibrium | gas | density | | | |
|
|
|
24.
|
Earth’s weather is created by gigantic ____________________ currents in
the atmosphere.
|
|
|
25.
|
The most abundant gas in Earth’s atmosphere is
____________________.
|
|
|
26.
|
Tungsten has a higher boiling point than alcohol because tungsten has higher
_________________________ forces than alcohol.
|
Short Answer
|
|
|
27.
|
Which forces are stronger, those bonding atoms together to form molecules or
those acting to hold molecules together?
|
|
|
28.
|
What causes pressure?
|
Problem
|
|
|
29.
|
Below is a set of axes representing the altitude above Earth’s surface on
the y-axis and the atmospheric pressure on the x-axis. Sketch a graph line representing
the relationship between these two variables. 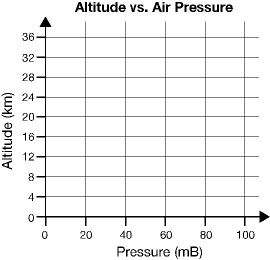
|
|
|
30.
|
The graph below was drawn using data recorded as water at -20ºC was heated
to 100ºC. On the graph, use letters A, B, C, and D to label the arrows pointing to those phases
or combination of phases represented from the list. A. Only ice is present B. Only liquid water
is present C. Ice and water are present D. Steam and water are present 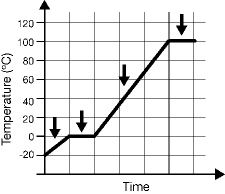
|
Essay
|
|
|
31.
|
Describe the properties of intermolecular
forces.
|
|
|
32.
|
Explain the difference between natural convection and forced convection.
|
|
|
33.
|
Explain the difference between boiling and evaporation.
|
Other
|
|
|
34.
|
The diagram below pictures a candle burning in a closed container. Using
arrows to represent the direction of air movement, sketch the convection currents that
would develop in the container as the candle continues to burn. Label warm air and cool air
currents. 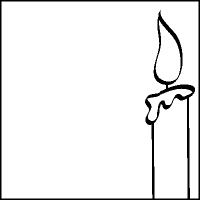
|