Modified True/False
Indicate
whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make
the statement true.
|
|
|
1.
|
The hottest part of the Sun is the corona.
_________________________
|
|
|
2.
|
To measure long distances, astronomers use a unit of length equal to the
distance light will travel in one year. Astronomers call it the astronomical unit.
_________________________
|
|
|
3.
|
Our sun is classified as a blue-colored star.
_________________________
|
Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
4.
|
The phrase “a giant, hot ball of gases” best describes a:
a. | planet. | b. | moon. | c. | star. | d. | meteorite. |
|
|
|
5.
|
The hottest part of the Sun is its:
a. | corona. | b. | core. | c. | chromosphere. | d. | photosphere. |
|
|
|
6.
|
Areas on the Sun representing cooler spots are called:
a. | coronas. | b. | solar constants. | c. | sunspots. | d. | auroras. |
|
|
|
7.
|
The source of the Sun’s heat and light energy is:
a. | combustion of helium gas. | b. | fusion of hydrogen nuclei. | c. | gravitational
pressure. | d. | burning of fossil fuels. |
|
|
|
8.
|
The source of heat and light energy produced by stars is:
a. | fission. | b. | fusion. | c. | internal
combustion. | d. | spontaneous regeneration. |
|
|
|
9.
|
The main characteristics used to classify stars include all of the following
EXCEPT:
a. | shape. | b. | brightness. | c. | color. | d. | temperature. |
|
|
|
10.
|
The color of the hottest stars is:
a. | red. | b. | orange. | c. | yellow. | d. | blue. |
|
|
|
11.
|
Although the Sun may look bright and white when you quickly look at it, the Sun
is classified by color as:
a. | red. | b. | yellow. | c. | orange. | d. | blue. |
|
|
|
12.
|
By size, the star known as our Sun is classified as:
a. | supergiant. | b. | giant. | c. | average. | d. | dwarf. |
|
|
|
13.
|
Scientists measure distances beyond our solar system (such as the distance
between two stars) using these units:
a. | meters | b. | kilometers | c. | astronomical
units | d. | light years |
|
|
|
14.
|
For continuous fusion of hydrogen to take place, extreme conditions must exist
in a star. These conditions include all of the following EXCEPT:
a. | a large helium source. | b. | high temperature. | c. | high
density. | d. | a large mass. |
|
|
|
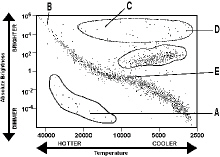 Figure 16-1A Figure 16-1A
|
|
|
15.
|
According to the H-R diagram in Figure 16-1A, the areas labeled B and E would be
classified as:
a. | red and blue supergiants | b. | the main sequence. | c. | white
dwarfs. | d. | red giants. |
|
|
|
16.
|
According to the H-R diagram in Figure 16-1A, the areas labeled C and D would be
classified as:
a. | red and blue supergiants. | b. | white dwarfs. | c. | the main
sequence. | d. | red giants. |
|
|
|
17.
|
As a group, stars known as main sequence stars on an H-R diagram are best
described as being:
a. | hotter. | b. | larger. | c. | stable. | d. | brighter. |
|
|
|
18.
|
Two stars have the same luminosity. The first star is one light year away from
your telescope. The second star is four light years away from your telescope. The first star’s
brightness is:
a. | four times as great as the second star’s. | b. | eight times as great
as the second star’s. | c. | sixteen times as great as the second
star’s. | d. | equal to the second star’s. |
|
|
|
19.
|
The brightness of the Sun when measured from various planets in the solar
system would be:
a. | greatest when measured at Mercury. | b. | greatest when measured at
Pluto. | c. | greatest when measured at Earth. | d. | the same at all
planets. |
|
|
|
20.
|
Sirius is about 8.8 light years from Earth. If one light year equals 9.46 ´ 1012 kilometers, how far is Sirius from Earth, measured in
kilometers?
a. | 8.3 ´ 1013 kilometers | b. | 1.1 ´ 1013 kilometers | c. | 8.3 ´
1011 kilometers | d. | 1.1 ´
1011 kilometers |
|
|
|
21.
|
The distance from Earth to the star Proxima Centauri is 4.01 ´ 1013 kilometers. What is this distance in light years? One
light year is equal to 9.46 ´ 1012 kilometers.
a. | 0.424 light years | b. | 4.24 light years | c. | 42.4 light
years | d. | 424 light years |
|
|
|
22.
|
If you were traveling at 30 kilometers per second, how long would it take to
reach Proxima Centauri, the nearest star to Earth other than our Sun? Proxima Centauri is 4.01 ´ 1013 kilometers from Earth. Hint: there are 31,557,600 seconds
in one year.
a. | Approximately 134 years | b. | Approximately 4,240 years | c. | Approximately 42,400
years | d. | Approximately 1,340,000,000,000 years |
|
Completion
Complete each
statement.
|
|
|
Select the correct term to complete each sentence. There are extra terms in
the list.| protostar | sunspots | fusion | | blue | red | spectroscope | | temperature | energy | neutron | | carbon | oxygen | helium | | hydrogen | supernova | camera | | | |
|
|
|
23.
|
Small, dark areas on the surface of the sun where the temperature is lower than
the surrounding surface area are known as ____________________.
|
|
|
24.
|
The source of the sun’s energy output is the process known as nuclear
____________________.
|
|
|
25.
|
Conditions needed for the continuous fusion of hydrogen in stars include
extremely high mass, high density, and high _________________________.
|
|
|
26.
|
The hottest stars in the universe are colored ____________________.
|
|
|
27.
|
The smallest stars, those with a diameter of 20 to 30 kilometers, are called
____________________ stars.
|
|
|
28.
|
The fusion of hydrogen in stars releases ____________________ and creates the
element helium.
|
Short Answer
|
|
|
29.
|
List the four main characteristics used to classify stars.
|
|
|
Use the H-R diagram below to answer the following questions: 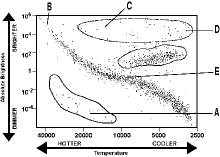 Figure 16-1A Figure 16-1A
|
|
|
30.
|
Which group of stars on the H-R diagram in Figure 16-1A is in the most stable
part of the star “life cycle”?
|
|
|
31.
|
On the H-R diagram in Figure 16-1A, which sections indicates white dwarfs?
Describe one significant difference between a typical white dwarf star and a typical red giant
star.
|
|
|
32.
|
Name the two by-products of the fusion of hydrogen nuclei that takes place at
the core of stars.
|
Problem
|
|
|
33.
|
The distance from Earth to the star Betelgeuse is 6.62 ´ 1015 kilometers. If one light year is equal to 9.46 ´ 1012 kilometers, what is the distance from Earth to Betelgeuse
in light years?
|
|
|
34.
|
The distance from Earth to the Triangulum galaxy is 2.6 million (2.6 ´ 106) light years. If one light year is equal to 9.46 ´ 1012 kilometers, what is the distance between Earth and the
Triangulum galaxy in kilometers?
|
|
|
35.
|
Two stars have the same luminosity. The first star is located 5 light years from
Earth. The second is 10 light years from Earth. Compare the brightness of the two stars as seen from
Earth.
|
Essay
|
|
|
36.
|
Explain the difference between the brightness and luminosity of stars.
|
|
|
37.
|
What is an H-R diagram and why is it important to astronomers?
|